Introduction
⚠️ END of lifer: Be very careful AWS QLDB is end of life anounced !
In the realm of distributed ledger technologies, AWS Quantum Ledger Database (QLDB) emerges as a promising solution bridging the gap between traditional databases and blockchain. This article delves deep into the concepts, use cases, and comparative analysis of QLDB with blockchain technology.
Main Concepts of QLDB
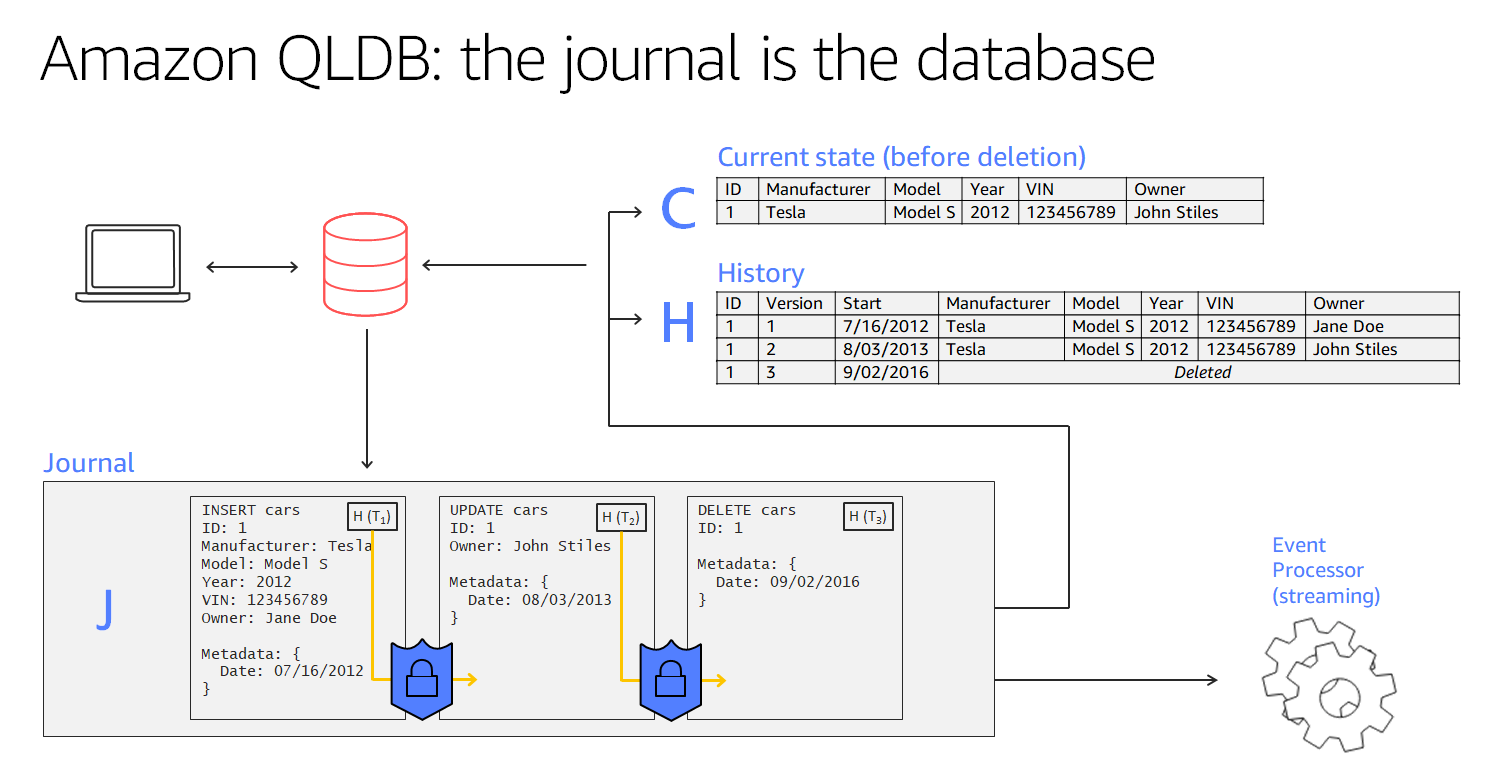
Immutable Journal
QLDB maintains an immutable journal of all transactions, akin to blockchain’s immutable ledger. Each transaction is cryptographically hashed and sequentially recorded, ensuring tamper-proof data integrity.
Transaction Digests
Every transaction in QLDB is associated with a unique hash value, termed as transaction digest. These digests serve as cryptographic fingerprints, enabling verification of transaction integrity and detecting unauthorized modifications.
Ledger
A ledger in QLDB represents a collection of tables that store data. Each ledger maintains its immutable history of transactions, providing a comprehensive audit trail of data modifications.
AWS Integration
QLDB seamlessly integrates with other AWS services, including AWS Lambda, AWS Key Management Service (KMS), and AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM). This integration facilitates secure data management and access control within the AWS ecosystem.
Use Cases of QLDB
Financial Transactions
QLDB is well-suited for applications requiring transparent and auditable financial transactions, such as banking, insurance, and accounting systems. Its immutable journal ensures data integrity and facilitates regulatory compliance.
Supply Chain Management
In supply chain management, QLDB enables tracking of product movements, verification of authenticity, and compliance with regulatory standards. Stakeholders can leverage QLDB to trace the origin and journey of products across the supply chain.
Identity and Access Management
QLDB serves as a trusted source of identity and access management data, maintaining records of user permissions, role assignments, and access control policies. Its immutable ledger capabilities enhance security and accountability in identity management.
Regulatory Compliance
Organizations operating in regulated industries, such as healthcare and government, can utilize QLDB to maintain compliance with industry-specific regulations. QLDB’s immutable journal and transaction digests provide verifiable evidence of compliance efforts.
Comparison with Blockchain
Centralized Control
Unlike public blockchains, QLDB is centrally managed by AWS, offering streamlined administration and governance. However, this centralized control may raise concerns regarding data ownership and vendor lock-in.
Performance and Scalability
QLDB boasts high performance and scalability, capable of handling thousands of transactions per second and dynamically scaling resources based on demand. In contrast, traditional blockchains may encounter scalability challenges due to their decentralized nature.
Data Privacy
QLDB provides granular control over data privacy and access permissions, enabling organizations to define fine-grained access policies and encryption settings. Public blockchains, while transparent, may not offer the same level of data privacy and confidentiality.
Cost
The cost of using QLDB is based on resource usage, such as storage, data transfer, and transaction volume. In comparison, deploying and maintaining a blockchain network can be more expensive due to infrastructure requirements and transaction fees.
When to Use QLDB vs. Blockchain
Use QLDB When
- Data integrity and auditability are paramount.
- High performance and scalability are required.
- Centralized control and administration are acceptable.
- Granular data privacy and access controls are needed.
- Seamless integration with AWS services is desired.
Use Blockchain When
- Decentralization and censorship resistance are critical.
- Trustless transactions and consensus are necessary.
- Public transparency and immutability are desired.
- Community-driven governance and consensus mechanisms are preferred.
- Interoperability with other blockchain networks is essential.
Conclusion
AWS Quantum Ledger Database (QLDB) offers a compelling alternative to traditional blockchain platforms, combining the transparency and immutability of blockchain with the scalability and performance of traditional databases. Whether you opt for QLDB or blockchain depends on your specific requirements, balancing factors like decentralization, performance, and data privacy.
Related Links
- AWS Quantum Ledger Database (QLDB)
- AWS QLDB Documentation
- AWS Blockchain Solutions
- Comparing Blockchain Solutions on AWS
- AWS Developer Resources
- AWS Architecture Center
- AWS Whitepapers
- AWS Training and Certification
This comprehensive guide sheds light on AWS Quantum Ledger Database (QLDB), empowering readers to make informed decisions regarding their database and blockchain needs. Whether you’re navigating the complexities of financial transactions or supply chain management, understanding the nuances of QLDB and blockchain technology is paramount in today’s digital landscape.